Iodination
![]()
Common Conditions:
SEAr (Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution)
Iodine is the least reactive halogen in aromatic substitutions, but sufficiently activated aromatic substrates (ex. anilines or phenols) readily react. The most common reagents are iodine and N-iodosuccinimide (NIS).
![]()
Lithiation / Iodination
Lithiation followed by electrophilic quench with iodine is a common method for iodination. Lithiation of substrates is typically carried out by organolithiums (ex. n-BuLi, s-BuLi, or t-BuLi) or a hindered lithium amide base (ex. LDA).
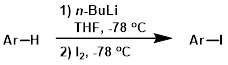
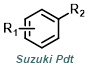
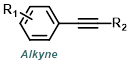
Reaction Map:
The reaction map is intended to provide insight into possible reactions one step before and after the title reaction. It also serves as an alternative way to navigate the website, and as a means of coming up with retrosynthetic ideas. Click on the reaction arrow to visit the page.
 |
||
 |
 |
|
 |
||
 |
References:
1) Clayden, J.; Organolithiums: Selectivity for Synthesis
2) Smith, M. B.; March's Advanced Organic Chemistry, 7th Edition