Mitsunobu
![]()
Common Conditions:
Aromatic Alcohols
Aromatic (phenolic) alcohols are the most common nucleophiles for Mitsunobu reactions. Reactions are typically done in THF with PPh3 and DEAD (or DIAD) at RT. Polymer supported PPh3 can be used to ease purification.[1]
![]()
Amides & Amide-like NH's
Amide NH's (or Amide-like NH's) that are sufficiently acidic can serve as nucleophiles in Mitsunobu reactions. Reactions are typically done in THF with PPh3 and DEAD (or DIAD) at RT. A common side reaction is the O-alkylation of the neighboring carbonyl(s). Polymer supported PPh3 can be used to ease purification.[1]
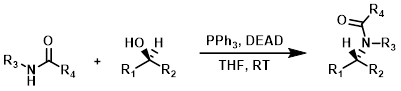
N-Heteroaryls
N-Heteroaryl NH's with sufficient acidity can undergo Mitsunobu reactions. Reactions are typically done in THF with PPh3 and DEAD (or DIAD) at RT. Polymer supported PPh3 can be used to ease purification.[1]
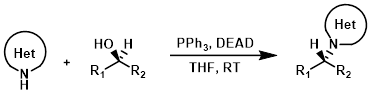
Azide
Diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA) is typically the source of azide for Mitsunobu reactions. Reactions are typically done in THF with PPh3 and DEAD (or DIAD) at RT. Polymer supported PPh3 can be used to ease purification.[1]

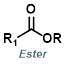
Reaction Map:
The reaction map is intended to provide insight into possible reactions one step before and after the title reaction. It also serves as an alternative way to navigate the website, and as a means of coming up with retrosynthetic ideas. Click on the reaction arrow to visit the page.
 |
||
 |
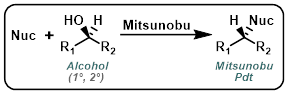 |
|
 |
||
 |
References:
1) Kurti, L.; Czako, B.; Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis