Curtius Rearrangement
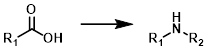
Common Conditions:
Boc Protected Pdt
Curtius Rearrangements in which the isocyanate intermediate is reacted with t-BuOH provides the Boc-Protected product. To control N2 evolution, large-scale reactions are typically run with dose-controlled addition of DPPA at a moderate temperature.[1][2]

Cbz Protected Pdt
Curtius Rearrangements in which the isocyanate intermediate is reacted with benzyl alcohol provides the Cbz-Protected product. To control N2 evolution, large-scale reactions are typically run with dose-controlled addition of DPPA at a moderate temperature.[1][2]
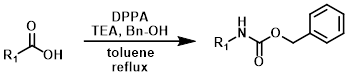
Urea Pdt
Curtius Rearrangements in which the isocyanate intermediate is reacted with an amine provides a urea product. To control N2 evolution, large-scale reactions are typically run with dose-controlled addition of DPPA at a moderate temperature.[1][2]
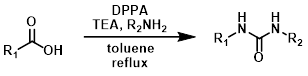
Reaction Map:
The reaction map is intended to provide insight into possible reactions one step before and after the title reaction. It also serves as an alternative way to navigate the website, and as a means of coming up with retrosynthetic ideas. Click on the reaction arrow to visit the page.
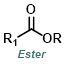 |
||
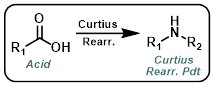 |
||
 |
||
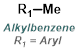 |
References:
1) Kurti, L.; Czako, B.; Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis
2) Anderson, N. G.; Practical Process Research and Development, a Guide for Organic Chemists, 2nd Edition