Benzoyl Peroxide
Other Names:
Dibenzoyl peroxide
BPO
General Information:
Structure:
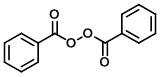
CAS Number: 94-36-0
Molecular Weight: 242.23 g/mol
Appearance: Colorless, crystalline solid
Melting Point: 105 C
Benzoyl peroxide is commonly used in organic chemistry as a radical initiator. It is an organic peroxide that readily undergoes homolysis to form free radicals. The O-O bond in benzoyl peroxide is relatively weak and can undergo homolysis when exposed to sufficient light or heat. Another common radical initiator is Azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN).

Common Uses:
Radical initiator for benzylic and allylic brominations

Procedure excerpt:
To a solution of the SM (261 mg, 1.00 mmol) in dry CCl4 (5 mL) in a 10 mL microwave vial was added benzoyl peroxide (12 mg, 0.05 mmol), followed by NBS . . .
Safety:
Benzoyl peroxide is potentially explosive, especially in pure form. For this reason, benzoyl peroxide is generally purchased commercially as a solid, wet with 25-30% H2O.
References:
1) Patent Reference: WO2012112946, page 165, ![]() (11.2 MB)
(11.2 MB)
2) Wikipedia: Benzoyl peroxide (link)
3) www.sigmaaldrich.com: Luperox A75, Benzoyl peroxide (link)
4) www.alfa.com: L13174 Benzoyl peroxide, 97% (dry wt.), wet with 25% water (link)