Dioxane
Other Names:
1,4-Dioxane
p-Dioxane
General Information:
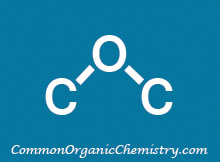
Structure:
![]()
CAS Number: 123-91-1
Molecular Weight: 88.11 g/mol
Appearance: Colorless liquid
Melting Point: 10-12 C
Boiling Point: 100-102 C
Density: 1.034 g/mL
Dioxane is a common aprotic solvent in organic chemistry. It is an ethereal solvent which is miscible with water. Dioxane can sometimes be a useful alternative to THF when a higher boiling point is desired. Commercially available 4M HCl in dioxane is one of the most frequently encountered applications of dioxane as a solvent. The use of 4M HCl in dioxane is common for boc deprotections.
Common Uses:
Solvent for reactions
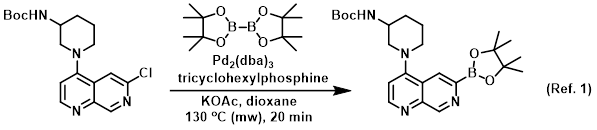
Procedure excerpt:
. . . the SM (1.0 equiv), KOAc (3.0 equiv), bis(pinacolato)diboron (2.0 equiv), tricyclohexylphosphine (0.8 equiv), and Pd2(dba)3 (0.2 equiv) in dioxane (0.06 M) was . . .
Safety:
Dioxane is irritating to the eyes and respiratory tract but has a low acute toxicity. It is considered by the EPA to be a probable human carcinogen. Dioxane is a flammable liquid.
References:
1) Patent Reference: WO2010026121, page 36, ![]() (3.6 MB)
(3.6 MB)
2) Wikipedia: 1,4-Dioxane (link)
3) www.sigmaaldrich.com: 1,4-Dioxane (link)