Potassium Carbonate
General Information:
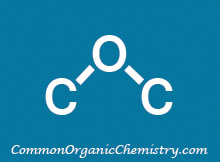
Structure:
![]()
CAS Number: 584-08-7
Molecular Weight: 138.21 g/mol
Appearance: White solid
Chemical Formula: K2CO3
Melting Point: 891 C
Potassium carbonate (K2CO3) is a commonly used base in organic chemistry. The pKa of its conjugate acid is 10.25. It is commonly used to deprotonate moderately acidic protons such as phenols (pKa ~10) and 1,3-dicarbonyl compounds (pKa ~9-13). Potassium carbonate has high solubility in water (1.12 g/mL, at 20 C), and has low solubility in ethanol, acetone, and many other common organic solvents.
Common Uses:
- Base for alkylations (including Benzyl Protections, SEM Protections, and Cbz Protections)
- Base for Pd Coupling reactions
- Base to neutralize acidic reaction mixtures prior to workup
Safety:
Potassium carbonate is considered a weak base. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. Potassium carbonate is relatively non-toxic.
References:
1) Wikipedia: Potassium carbonate (link)
2) www.sigmaaldrich.com: Potassium carbonate (link)
3) Reich, H. J.; Rigby, J. H.; Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Acidic and Basic Reagents