TBS Protection
Common Conditions (Protection):
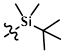
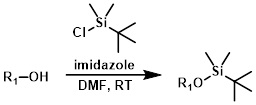
TBS-Cl
TBS-Cl effectively protects primary and secondary alcohols (not tertiary). TBS-Cl reacts very slowly when used without basic activators (ex. imidazole or DMAP). DMF is the most common solvent.[1]
TBS-OTf
TBS-OTf is a very powerful silylating agent, and is capable of protecting primary, secondary, and teriary alcohols. The base is usually 2,6-lutidine and the solvent DCM.[1]

Common Conditions (Deprotection):
TBAF
Tetrabutylammonium fluoride (TBAF) is the most popular fluoride reagent for TBS deprotection. The basicity of fluoride can sometimes cause undesired side reactions.[1]
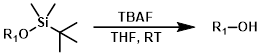
HCl
HCl effectively removes TBS groups. MeOH is often used as the solvent. Other acid sensitive functionalities may also be affected.[1]

Cs2CO3
Cs2CO3 (or K2CO3) is sometimes used to deprotect phenolic TBS ethers. Sometimes phenolic TBS ethers can be selectively deprotected in the presence of alkyl TBS ethers.[1][2]
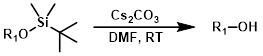
References:
1) Kocienski, P. J.; Protecting Groups, 3rd Edition
2) Wuts, P. G. M.; Greene, T. W.; Greene's Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis, 4th Edition