Boc Deprotection
(HCl)
Mechanism:
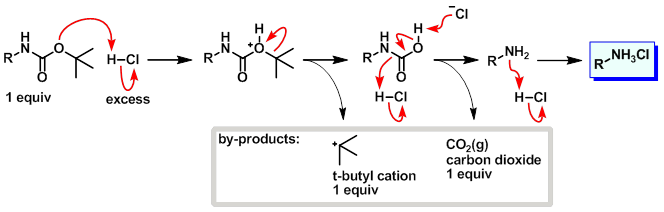
Steps:
- The tert-butyl carbamate becomes protonated.
- Loss of the tert-butyl cation results in a carbamic acid.
- Decarboxylation of the carbamic acid results in the free amine.
- Protonation of amine under the acidic conditions provides the pdt as the HCl salt.
Key Points:
- The tert-butyl cation will either be quenched by a suitable trapping agent, deprotonate to form isobutylene (gas), or polymerize to form isobutylene oligomers.
- The CO2 gas that forms during the reaction should be allowed to escape. Don't run boc deprotections in closed systems.