TFA
(Trifluoroacetic Acid)
Other Names:
2,2,2-Trifluoroethanoic acid
Trifluoroethanoic acid
General Information:
Structure:
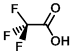
CAS Number: 76-05-1
Molecular Weight: 114.02 g/mol
Appearance: Colorless liquid
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is a strong organic acid typically used as a solvent or acid catalyst. TFA is the CF3 analogue of acetic acid (AcOH) which due to the electron withdrawing effect of the fluorine atoms is much more acidic than AcOH. The pKa of TFA is 0.23, compared to a pKa of 4.76 for AcOH. The low boiling point (bp = 72 C) of TFA facilitates simpler product isolation due to the fact that it can be removed via concentration on rotovap.
Common Uses:
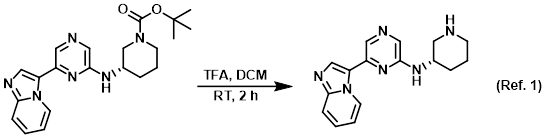
Reagent for boc deprotections
Reagent for SEM deprotections
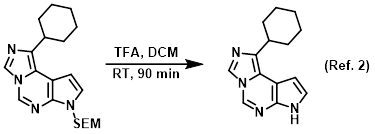
Reagent for benzyl deprotections
Reagent for PMB deprotections
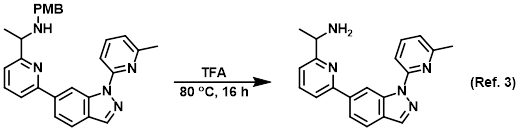
Reagent for trityl deprotections
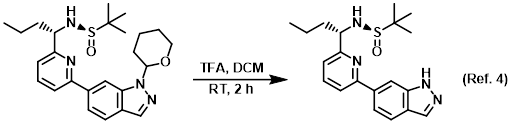
Reagent for THP deprotections
Reagent for the reduction of alcohols (TFA + Et3SiH)
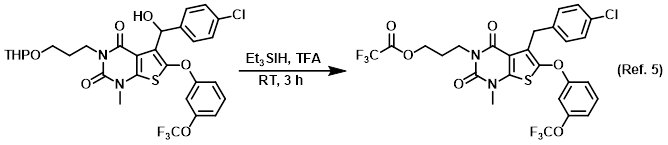
Safety:
Trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) is an extremely corrosive acid which causes severe damage when in contact with skin, eyes, and tissue of mucous membrane.
References:
1) Patent Reference: WO2010016005, page 83, ![]() (11.3 MB)
(11.3 MB)
2) Patent Reference: WO2012149280, page 54, ![]() (4.1 MB)
(4.1 MB)
3) Patent Reference: WO2016011390, page 105, ![]() (20.2 MB)
(20.2 MB)
4) Patent Reference: WO2016011390, page 319, ![]() (20.2 MB)
(20.2 MB)
5) Patent Reference: WO2016023832, page 41, ![]() (3.2 MB)
(3.2 MB)
6) Reich, H. J.; Rigby, J. H.; Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Acidic and Basic Reagents
7) Wikipedia: Trifluoroacetic acid (link)
8) www.sigmaaldrich.com: Trifluoroacetic acid (link)