Alcohol to Ketone
(Dess-Martin Periodinane)
Mechanism:
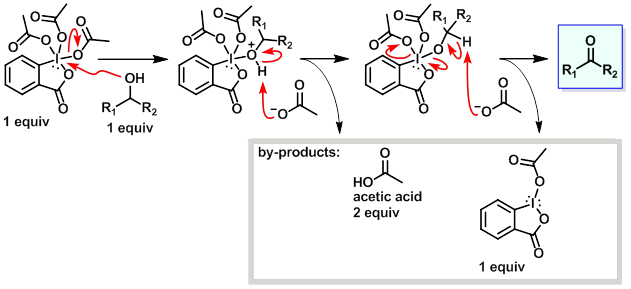
Steps:
- The alcohol displaces an acetate from the Dess-Martin reagent.
- The proton on the now positively charged oxygen atom of the alcohol is picked up by an acetate molecule.
- Another molecule of acetate removes the proton attached to the carbon atom leading to the formation of the carbon oxygen double bond of the ketone. The process leads to a release of another acetate molecule and a mono-acetoxy iodinane.
Key Points:
- Two equivalents of acetic acid form during the rxn. If a substrate is sensitive to these mildly acidic conditions, then a base such as NaHCO3 or pyridine can be used to buffer the rxn.
- The mono-acetoxy iodinane by-pdt can be converted to easier to remove by-pdts during work-up by treatment with aq NaOH or Na2S2O3.