Sodium Azide
Other Names:
Hydrazoic acid sodium salt
General Information:
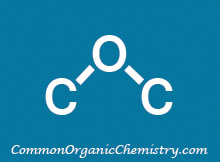
Structure:
![]()
CAS Number: 26628-22-8
Molecular Weight: 65.01 g/mol
Appearance: White solid
Chemical Formula: NaN3
Sodium azide is versatile reagent for a variety of synthetic transformations. A common use is for the formation of azides via substitution or SNAr reactions. These azides are often then reduced to give the corresponding amine products. Sodium azide is also used in a number of cyclization reactions, such as the formation of triazoles or tetrazoles. Sodium azide can also be used for Curtius rearrangements but generally other azide sources such as diphenylphosphoryl azide (DPPA) are employed.
Sodium azide is highly toxic and should be handled very carefully. Azides in general are known to have the potential to decompose explosively. Always consider alternative chemistry before using sodium azide.
Common Uses:
Nucleophile in substitution reactions

Procedure excerpt:
To a solution of the SM (0.3 g, 0.97 mmol) in DMF (10 mL) was added NaN3 (127 mg, 1.94 mmol) at 0 C. The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 16 h. The mixture was . . .
Nucleophile in SNAr reactions

Procedure excerpt:
To a stirring solution of the SM (100 mg, 0.15 mmol) in DMF (5 mL) was added NaN3 (50 mg, 0.7 mmol) and the reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 3 h. The mixture was . . .
Safety:
Sodium azide is very toxic and should be handled with extra care. Sodium azide, as well as related azides, can decompose explosively. Large scale reactions with sodium azide are not recommended.
References:
1) Patent Reference: WO2014149164, page 398, ![]() (23.7 MB)
(23.7 MB)
2) Patent Reference: WO2015129926, page 267, ![]() (21.5 MB)
(21.5 MB)
3) Wikipedia: Sodium azide (link)