Barium Hydroxide
General Information:
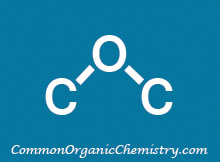
Structure:
Ba(OH)2
CAS Number: 17194-00-2 (anhydrous)
22326-55-2 (monohydrate)
12230-71-6 (octahydrate)
Molecular Weight:171.34 g/mol (anhydrous)
189.355 g/mol (monohydrate)
315.46 g/mol (octahydrate)
Appearance: White solid (monohydrate)
Transparent crystals or white masses (octahydrate)
Melting Point: 78 C (octahydrate)
Basicity (pKb): 0.15 (first -OH), 0.64 (second -OH)
The octahydrate of barium hydroxide is freely soluble in water and MeOH, whereas the monohydrate is only slightly soluble in water. For this reason the octahydrate is the most common form.
Common Uses:
Base/reagent for the hydrolysis of nitriles to carboxylic acids

Procedure excerpt:
A mixture of the SM (2.4 g, 11 mmol) and Ba(OH)2-8H2O (5.3 g, 17 mmol) in H2O (100 mL) was heated at reflux for 5 days. The mixture was cooled . . .
Safety:
Barium hydroxide is a strong base. Similar to other strong bases, barium hydroxide is very corrosive and causes extreme damage to eyes, skin, mucous membranes, and the upper respiratory tract.
References:
1) Patent Reference: WO2016014463, page 68, ![]() (6.7 MB)
(6.7 MB)
2) Reich, H. J.; Rigby, J. H.; Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis, Acidic and Basic Reagents
3) Wikipedia: Barium hydroxide (link)
4) www.sigmaaldrich.com: Barium hydroxide octahydrate (link)