Acetonitrile
Other Names:
ACN
Methyl cyanide
General Information:
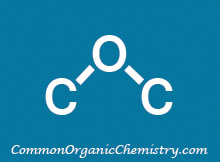
Structure:
![]()
CAS Number: 75-05-8
Molecular Weight: 41.05 g/mol
Appearance: Colorless liquid
Chemical Formula: CH3CN
Melting Point: -48 C
Boiling Point: 80-82 C
Density: 0.786 g/mL
Acetonitrile (ACN) is a polar aprotic solvent used for a variety of different reactions. Common reactions employing ACN as a solvent include substitutions, SNAr reactions, brominations, and iodinations. Acetonitrile is also widely used as part of the mobile phase in HPLC and LCMS. The use of ACN as a reagent is not very common, but one example is in Ritter reactions.
Common Uses:
Solvent for reactions

Procedure excerpt:
A mixture of the alkyl bromide (A) (200 mg, 0.810 mmol), the amine (B) (98 mg, 0.810 mmol), and K2CO3 (336 mg, 2.429 mmol) in ACN (20 mL) was stirred . . .
Solvent (mobile phase) for reverse phase purifications

Procedure excerpt:
. . . it was concentrated and purified by reverse phase HPLC (20-95% 0.1% TFA/ACN in 0.1% TFA/H2O) to provide the product as a yellow . . .
Reagent in Ritter reactions

Safety:
Acetonitrile (ACN) is slightly/moderately toxic. It can be metabolized in the body to hydrogen cyanide, but cases of acetonitrile poisoning are not common. Acetonitrile is highly flammable.
References:
1) Patent Reference: WO2016011930, page 173, ![]() (15.7 MB)
(15.7 MB)
2) Patent Reference: WO2012129338, page 151, ![]() (12.0 MB)
(12.0 MB)
3) Wikipedia: Acetonitrile (link)
4) www.sigmaaldrich.com: Acetonitrile (link)
5) www.alfa.com: A19862 Acetonitrile, 99% (link)
6) Kurti, L.; Czako, B.; Strategic Applications of Named Reactions in Organic Synthesis